iCare articles
-
Find Your Local iCare USA Sales Representative
Contact us -
iCare Products
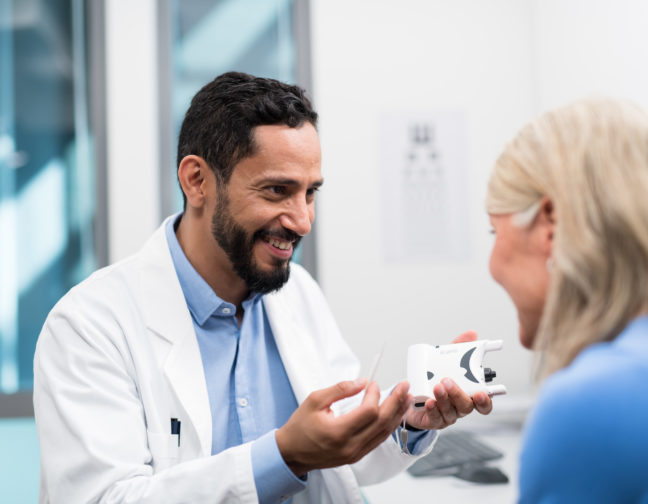
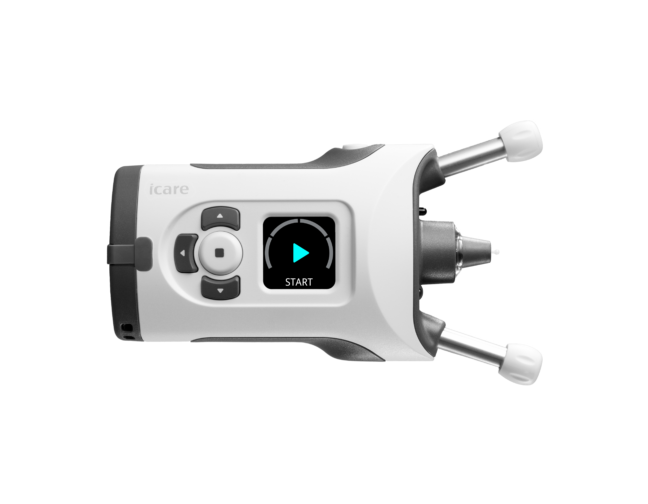
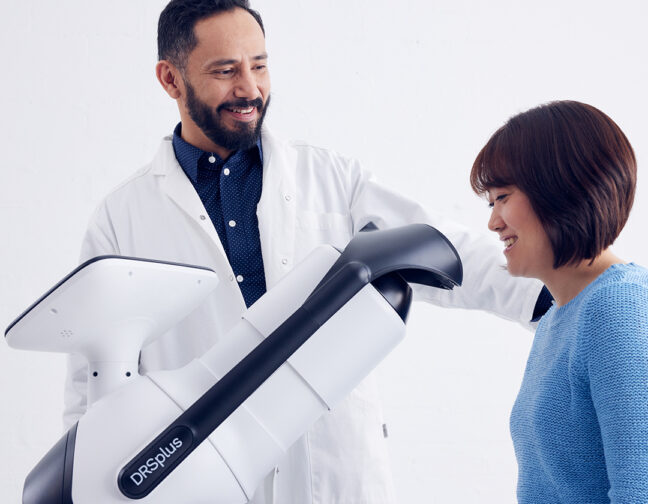
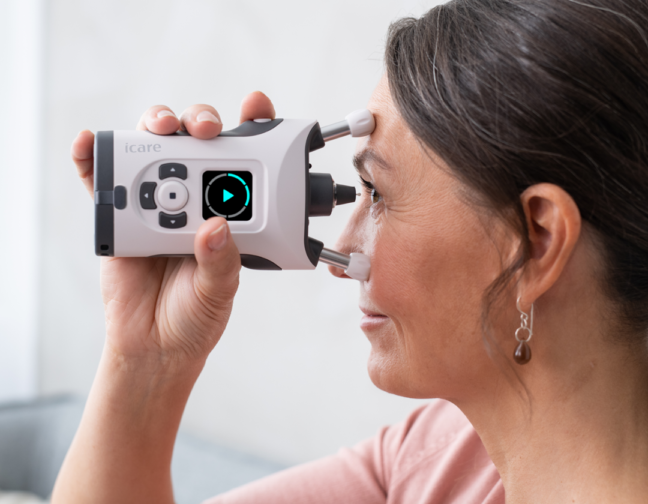
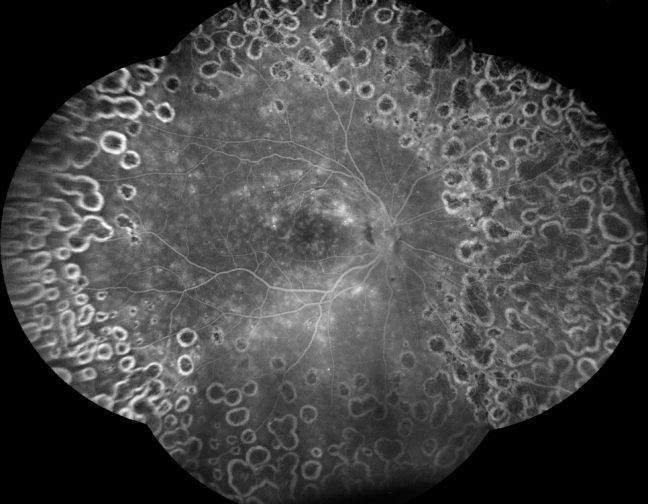
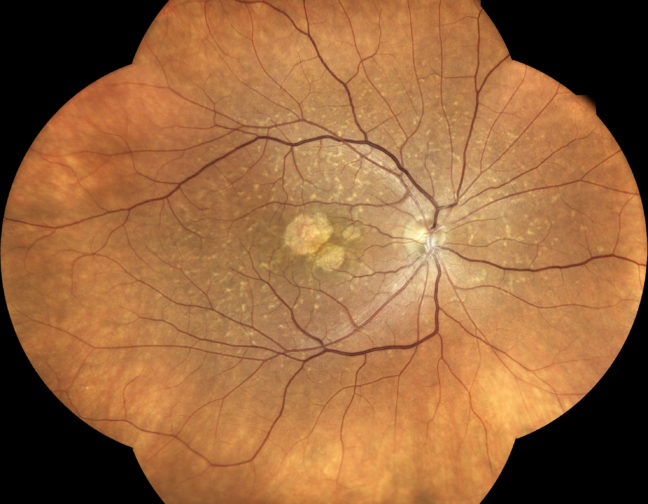
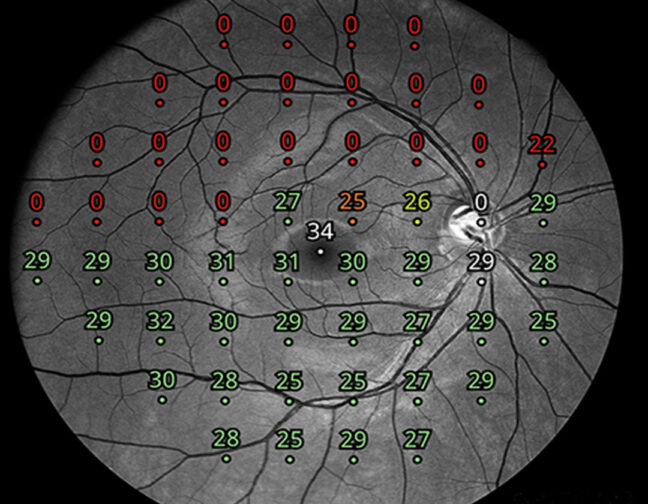
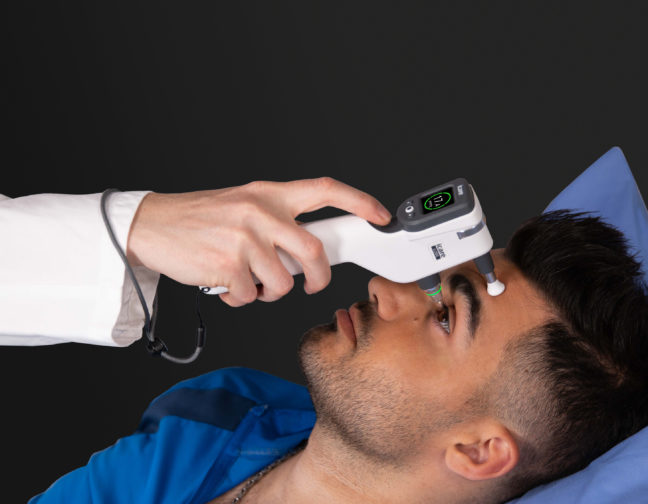
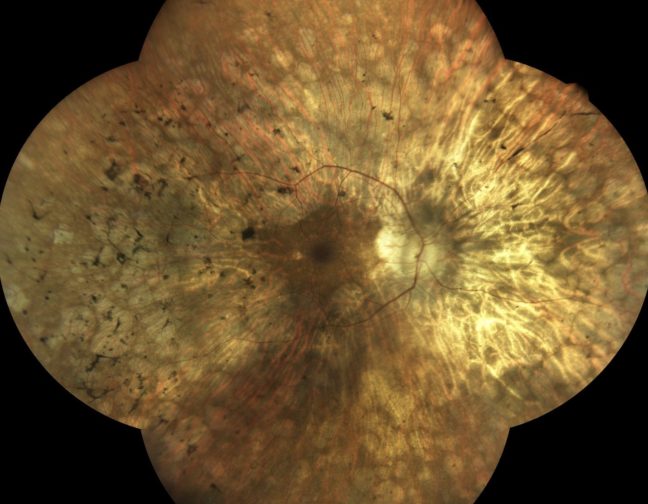
iCare provides eye doctors with the latest solutions for comprehensive screening, diagnostics and monitoring of glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and macular degeneration (AMD).
Read more